
Main achievements
Research Project 1: Establishment of the basis for advanced genome analysis technology and promotion of translational studies for conquering immunological and allergic diseases
- Chips with micro-channels made of synthetic resin have been developed for the separation of blood cells by applying microfluidics, injection molding, and hydrophilic surface treatment technology. Also, a protein array device with fluorescence detection has been developed by combining the cDNA clones for human proteins stored at Kazusa DNA Research Institute, HaloTag technology, and light patterning technology with a light-sensitive coating agent. Prototypes of vapor-deposition apparatus and of filtration chip/apparatus have been produced as byproducts.
- To establish a gene screening center, analysis of genes causing a hyper IgE syndrome, a syndrome caused by hereditary immunodeficiency, has already been started after developing technology for the condensation of target regions. Consequently, the sequencing time has markedly been reduced.
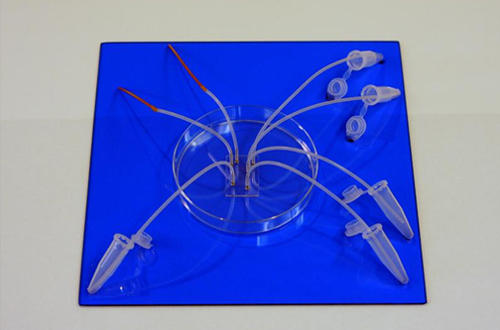
A prototype of a blood-separating chip

A deposition apparatus for hydrophilic surface-coating: patent has been applied by Kazusa DNA Research Institute, Waseda University, and TI Co., Ltd.
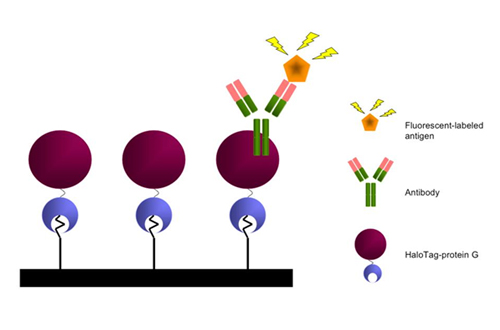
A schematic illustration of protein array
Research Project 2: Research and development of biomarkers for predicting treatment efficacy and prognosis of refractory immune/allergy-related diseases
Protocols for clinical studies on refractory allergic diseases and cancers were prepared and subjected to the examination by the ethics committee: clinical studies were started after receiving its approval. Three biomarkers for cancer have thus been identified by analyzing gene expression of the samples obtained from a small number of cancer patients. A patent application (tokugan No. 2009-200911) has been filed.
Research Project 3: Development and application of next-generation model mice for human diseases

- A method has been established for acquiring ES cells from NOD/SCID mice (tokugan No. 2010-985668).
- Human hematopoietic factor and cytokine gene-infected mice were backcrossed, and the expression of human-type genes was confirmed at the protein level.
Copyright (C) 2009 - 2011 All rights reserved Kazusa DNA Research Institute